Intro
- manager for Node.js packages (or modules)
- package contains all the files you need for a module, modules are JavaScript libraries to include in project
npm install package-name , then var pn = require('package-name'); in app files- NPM creates a folder named "node_modules", where the package will be placed, all future packages will be placed in this folder
- npmjs.org
- search.npmjs.org
- add private:true to package.json to prevent accidental publication of private repositories as well as suppressing any warnings generated when running npm install
- save a package as a devDependency by specifying a
--save-dev flag, packages used for development purposes (running tests, transpiling code,...)
# search packages
npm search mp3
# view details
npm view express
# show all installed packages
npm list
npm list depth 1 # further dependencies depth level
npm list -g # Globally
npm list -g --depth=0
# installing Latest Module
npm install package-name
npm install package-name -g # Globally
# install packages as a developer dependency
npm install package-name --save-dev
# install Specific Module Version
npm install package-name@0.2.6
# install Specific Module Version Range
npm install package-name@0.2.x
# Install package.json Dependencies
npm install -d
# Uninstalling a Module
npm uninstall package-name
npm uninstall package-name -g # Globally
# Updating an Installed Module
npm update package-name
npm update package-name -g
# update all packages
npm update
# check the registry if installed packages are currently outdated
npm outdated
# aliases
npm i package-name # install local package
npm i -g package-name # install global package
npm un package-name # uninstall local package
npm up # npm update packages
npm t # run tests
npm ls # list installed modules
npm ll # print additional package information while listing modules
npm la
# install multiple packages at once
npm i express momemt lodash mongoose body-parser webpack
# folder as npm package, package.json is the project manifest file
npm init
npm init -y # quicker way
# it is recommended that you give your user account
# access to the /usr/local folder instead
# so that you can just issue normal commands in there
sudo chown -R $USER /usr/local
# --- OR change the Location of Global Packages
# npm global configuration
npm config list
# get config
npm config get prefix # is /usr for example
# set config
# install global packages in our home directory
cd ~ && mkdir .node_modules_global
npm config set prefix=$HOME/.node_modules_global
# and install npm again
npm install npm --g
# add .node_modules_global/bin to our $PATH environment variable,
# so that we can run global packages from the command line
# append the following line
# to your .profile, .bash_profile or .bashrc and restarting your terminal
export PATH="$HOME/.node_modules_global/bin:$PATH"
# now our .node_modules_global/bin will found first
# and the correct version of npm will be used
which npm
# npm keeps a copy of installed package
# copies are cached in the .npm directory in your home path
ls ~/.npm
# clean it up
npm cache clean
# purge all node_module folders from your workspace
# if you have multiple node projects
find . -name "node_modules" -type d -exec rm -rf '{}' +
# running project
npm test
npm run start # run "start" script specified in package.json
npm run test # run Jest test against all .test.ts or .spec.ts files ("test" script)
npm run build # run a production build generation ("build folder")
# server runs at http://localhost:3000
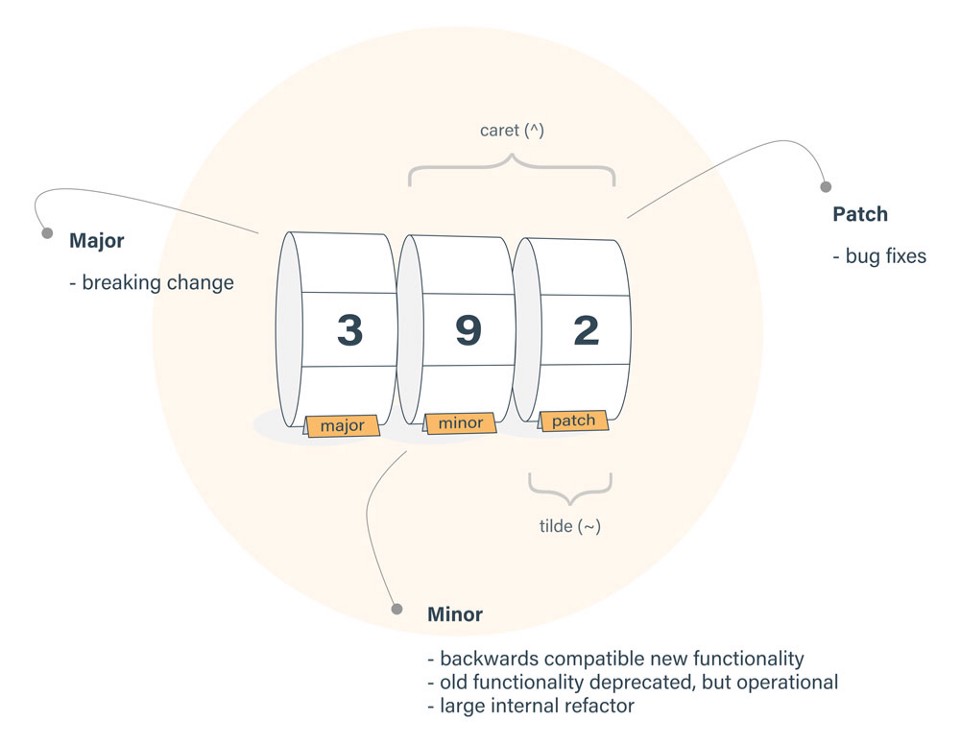
Semantic Versioning
serve - static file serving and directory listing
npm install -g serve
serve -s build # serve static site on the port 5000
serve -s build -l 4000 # adjust port
http-server
npm install http-server -g
http-server -p 8080 -c-1 dist/project-name
http-server -p 8080 -c-1 dist/project-name/index.html
./node_modules/.bin/http-server -a localhost -p 8000
# COMMAND DESCRIPTION:
#
# http-server [path] [options]
#
# [path]
# defaults to ./public if the folder exists, and ./ otherwise
#
# [options]
# -a - address to use (defaults to 0.0.0.0)
# -p - port to use (defaults to 8080)
# -d - show directory listings (defaults to 'True')
# -i - display autoIndex (defaults to 'True')
# -g or --gzip - when enabled (defaults to 'False')
# will serve ./public/some-file.js.gz
# in place of ./public/some-file.js
# when a such file exists and request accepts gzip encoding
# -e or --ext - default file extension if none supplied (defaults to 'html')
# -s or --silent - suppress log messages from output
# --cors - enable CORS via the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header
# -o - open browser window after starting the server
# -c - set cache time (in seconds) for cache-control max-age header
# -c10 for 10 seconds (defaults to '3600'), to disable caching, use -c-1
# -U or --utc - use UTC time format in log messages
# -P or --proxy - proxies all requests which cant be resolved
# locally to the given url. e.g.: -P http://someurl.com
# -S or --ssl - enable https
# -C or --cert - path to ssl cert file (default: cert.pem)
# -K or --key - path to ssl key file (default: key.pem)
# -r or --robots - provide a /robots.txt (defaults to 'User-agent: *\nDisallow: /')
# -h or --help - print this list and exit
Back to Main Page
